Difference between revisions of "Support:Documents:Examples:Estimate physiological parameters using a physiologically based model"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
cm = addParameter(cm, 'pfeng', [delay a lambda]'); | cm = addParameter(cm, 'pfeng', [delay a lambda]'); | ||
| + | |||
| + | % Define input function | ||
cm = addInput(cm, 'Cp', 'sa', 'dk', 'fengInputByPar','pfeng'); % Cp is the plasma input function | cm = addInput(cm, 'Cp', 'sa', 'dk', 'fengInputByPar','pfeng'); % Cp is the plasma input function | ||
cm = addInput(cm, 'Ca',1,0, 'fengInputByPar', 'pfeng'); % Ca is the decay-corrected whole-blood input function. Herein, we assume that Cp=Ca. | cm = addInput(cm, 'Ca',1,0, 'fengInputByPar', 'pfeng'); % Ca is the decay-corrected whole-blood input function. Herein, we assume that Cp=Ca. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 82: | ||
cm=addOutput(cm,'TissueTotal',wlistTotal,xlistTotal); | cm=addOutput(cm,'TissueTotal',wlistTotal,xlistTotal); | ||
| + | % Define model parameters to be esimated | ||
cm=addSensitivity(cm,'k1','ISg','ICg','Fis','Fb'); | cm=addSensitivity(cm,'k1','ISg','ICg','Fis','Fb'); | ||
| Line 100: | Line 103: | ||
cm = set(cm, 'OptimizerOptions', oo); | cm = set(cm, 'OptimizerOptions', oo); | ||
| − | % Set initial conditions and | + | % Set initial conditions and bounds |
| − | % k1, ISg, ICg, Fs, | + | % k1, ISg, ICg, Fs, Fb |
pinit = [0.01 ; 4.4 ; 0.1 ;0.15 ; 0.01]; | pinit = [0.01 ; 4.4 ; 0.1 ;0.15 ; 0.01]; | ||
plb = [0.001; 1 ; 0.001;0.10 ; 0 ]; | plb = [0.001; 1 ; 0.001;0.10 ; 0 ]; | ||
| Line 122: | Line 125: | ||
legend('Noisy data', 'Model fit'); | legend('Noisy data', 'Model fit'); | ||
| − | Pg=6;KGa=14;KHa=0.17;KGg=3.5;KHg=0.13; % | + | Pg=6;KGa=14;KHa=0.17;KGg=3.5;KHg=0.13; % Units are mM |
k1=pfit(1);k2=pfit(1)/pfit(4);ISg=pfit(2);ICg=pfit(3);Fis=pfit(4);Fb=pfit(5); | k1=pfit(1);k2=pfit(1)/pfit(4);ISg=pfit(2);ICg=pfit(3);Fis=pfit(4);Fb=pfit(5); | ||
| + | |||
| + | % Physiological parameters | ||
VG=(k1*ISg-k1*Pg)/(ICg/(KGg+ICg)-ISg/(KGg+ISg)) | VG=(k1*ISg-k1*Pg)/(ICg/(KGg+ICg)-ISg/(KGg+ISg)) | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 22 August 2011
Estimation of Physiological Parameters Using a Physiologically Based Model
Overview
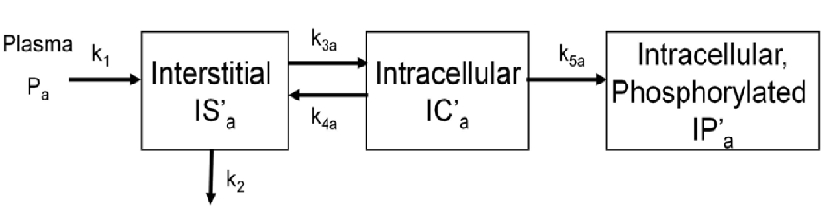
To evalute glucose trasnport and phosphorylation in skeletal muscle,a physiologically based model has been proposed by our group. The below figure shows the kinetics of a phosphorylatable glucsoe analog (e.g. 18F-labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose) in skeletal muscle. The model has three tissue compartments with five rate constants.
Example of Implementation of the Physiologically Based Model
Here, we show an example of implementation of the proposed model using COMKAT.
cm=compartmentModel;
% Define parameters
cm=addParameter(cm,'k1',0.1);
cm=addParameter(cm,'k2','k1/Fis');
cm=addParameter(cm,'k3','VG/(Fis*KGa+Fis*ISg*KGa/KGg)');
cm=addParameter(cm,'k4','VG/(Fic*KGa+Fic*ICg*KGa/KGg)');
cm=addParameter(cm,'k5','VH/(Fic*KHa+Fic*ICg*KHa/KHg)');
cm=addParameter(cm,'Fb',0.02); % fraction of total space occupied by blood
cm=addParameter(cm,'Fis',0.3); % fraction of total space occupied by interstitial space
cm=addParameter(cm,'Fic','1-Fis-Fb'); % fraction of total space occupied by intracellular space
cm=addParameter(cm,'F',1);
cm=addParameter(cm,'Pg',6); % Plasma glucose concentration (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'ISg',5.4); % Interstitial glucose concentration (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'ICg',0.2); % Intracellular glucose concentration (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'KGg',3.5); % Michaelis constant of glucose transporter (GLUT) for glucose (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'KHg',0.13); % Michaelis constant of hexokinase for glucose (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'KGa',14); % Michaelis constant of glucose transporter (GLUT) for glucose analog (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'KHa',0.17); % Michaelis constant of hexokinase for glucose analog (mM)
cm=addParameter(cm,'VG','(k1*Pg-k1*ISg)/(ISg/(KGg+ISg)-ICg/(KGg+ICg))'); % Maximal velocity of glucose transport for glucose=6FDG=2FDG
cm=addParameter(cm,'VH','(k1*Pg-k1*ISg)/(ICg/(KHg+ICg))'); % Maximal velocity of glucose phosphorylation for glucose=6FDG=2FDG
% Specific activity (sa): if the unit of image data is the same with that of input function, the specific activity is 1.
cm=addParameter(cm,'sa',1);
% Usually, the decay time correction of image data is performed. So, dk is zero.
cm=addParameter(cm,'dk',0);
% Define scan time (minutes)
delay = 0.0;
scanduration = 120;
t=[ones(5,1)/30;ones(10,1)/12;ones(12,1)*0.5;ones(8,1);ones(21,1)*5];
scant = [[0;cumsum(t(1:(length(t)-1)))] cumsum(t)];
scanTime = [scant(:,1),scant(:,2)];
cm = set(cm, 'ScanTime', scanTime);
lambda = [-12.02 -2.57 -0.02];
a = [1771.5 94.55 14.27];
cm = addParameter(cm, 'pfeng', [delay a lambda]');
% Define input function
cm = addInput(cm, 'Cp', 'sa', 'dk', 'fengInputByPar','pfeng'); % Cp is the plasma input function
cm = addInput(cm, 'Ca',1,0, 'fengInputByPar', 'pfeng'); % Ca is the decay-corrected whole-blood input function. Herein, we assume that Cp=Ca.
% Define compartment
cm=addCompartment(cm,'IS'); % interstitial
cm=addCompartment(cm,'IC'); % intracellular
cm=addCompartment(cm,'IP'); % intracellular phosphorylated
cm=addCompartment(cm,'Junk');
% Define link
cm=addLink(cm,'L','Cp','IS','k1');
cm=addLink(cm,'K','IS','Junk','k2');
cm=addLink(cm,'K','IS','IC','k3');
cm=addLink(cm,'K','IC','IS','k4');
cm=addLink(cm,'K','IC','IP','k5');
% Define output obtained from each normalized compartment
wlistTotal={'IS','F';'IC','F';'IP','F'};
xlistTotal={'Ca','Fb'};
cm=addOutput(cm,'TissueTotal',wlistTotal,xlistTotal);
% Define model parameters to be esimated
cm=addSensitivity(cm,'k1','ISg','ICg','Fis','Fb');
[PET,PETIndex,Output,OutputIndex]=solve(cm);
noise_level=0.05;
sd=noise_level*sqrt(PET(:,3)./(PET(:,2)-PET(:,1)));
data=sd.*randn(size(PET(:,3)))+PET(:,3);
cm=set(cm,'ExperimentalData',data);
cm = set(cm,'ExperimentalDataSD',sd);
optsIRLS = setopt('SDModelFunction', @IRLSnoiseModel);
cm = set(cm, 'IRLSOptions', optsIRLS);
oo = optimset('TolFun', 1e-8, 'TolX', 1e-4,'Algorithm','interior-point');
cm = set(cm, 'OptimizerOptions', oo);
% Set initial conditions and bounds
% k1, ISg, ICg, Fs, Fb
pinit = [0.01 ; 4.4 ; 0.1 ;0.15 ; 0.01];
plb = [0.001; 1 ; 0.001;0.10 ; 0 ];
pub = [0.5 ; 6 ; 1 ;0.60 ; 0.04];
[pfit, qfit, modelfit, exitflag, output, lambda, grad, hessian, objfunval] = fitGen(cm, pinit, plb, pub, 'IRLS');
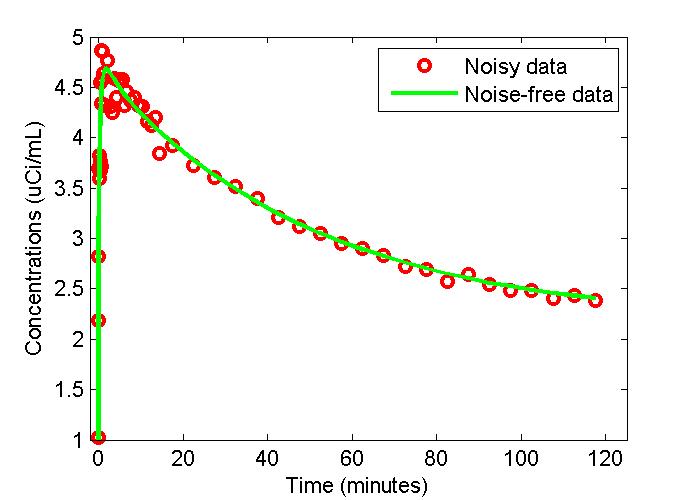
figure;
t = 0.5*(PET(:,1)+PET(:,2));
plot(t,PET(:,3),'g-',t,data,'ro','LineWidth',2);
xlabel('Time (minutes)');
ylabel('Concentrations (uCi/mL)');
legend('Noisy data','Noise-free data');
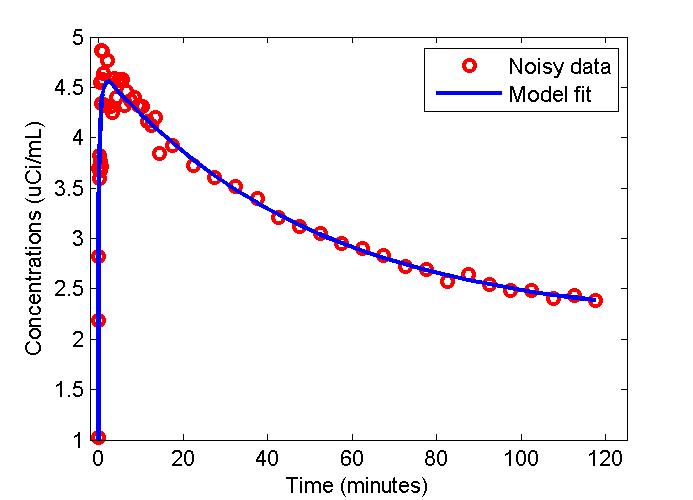
figure;
t = 0.5*(PET(:,1)+PET(:,2));
plot(t,data,'ro',t,modelfit,'b-','LineWidth',2);
xlabel('Time (minutes)');
ylabel('Concentrations (uCi/mL)');
legend('Noisy data', 'Model fit');
Pg=6;KGa=14;KHa=0.17;KGg=3.5;KHg=0.13; % Units are mM
k1=pfit(1);k2=pfit(1)/pfit(4);ISg=pfit(2);ICg=pfit(3);Fis=pfit(4);Fb=pfit(5);
% Physiological parameters
VG=(k1*ISg-k1*Pg)/(ICg/(KGg+ICg)-ISg/(KGg+ISg))
VH=(k1*Pg-k1*ISg)/(ICg/(KHg+ICg))
CI=VG*ISg/(KGg+ISg)
CE=VG*ICg/(KGg+ICg)
PR=VH*ICg/(KHg+ICg)